
Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding (bruising, tarry stools, sudden drop in blood pressure, petechiae, blood in urine, etc.More than 3 million Americans have atrial fibrillation, a problem with the electrical system of the heart that causes an irregular heart rhythm.Do not take with NSAIDS/aspirin, alcohol, or other agents that may also cause bleeding.Patients with mechanical heart valves can have INRs as high as 3.5.
 Therapeutic level of INR is between 2.0-3.0. INR (international normalized ratio) is a normalized ratio of (patient’s PT)/(international average PT). Patients may receive heparin concurrently until warfarin has had time to reach a therapeutic level (known as “heparin bridge”) Inhibits the liver’s synthesis of vitamin K, which plays a role in decreasing prothrombin and several clotting factors. In cases where we want warfarin’s effects to be reversed, vitamin K can be given as an injection or through an IV. This is because vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin. And finally, patients taking warfarin should avoid eating an excess amount of leafy greens, and other foods high in vitamin K. Warfarin is also teratogenic and should not be given to pregnant patients. A therapeutic INR level for a patient on warfarin is between 2 and 3. To reduce the risk of severe bleeding, patients are monitored using the PT and INR levels.
Therapeutic level of INR is between 2.0-3.0. INR (international normalized ratio) is a normalized ratio of (patient’s PT)/(international average PT). Patients may receive heparin concurrently until warfarin has had time to reach a therapeutic level (known as “heparin bridge”) Inhibits the liver’s synthesis of vitamin K, which plays a role in decreasing prothrombin and several clotting factors. In cases where we want warfarin’s effects to be reversed, vitamin K can be given as an injection or through an IV. This is because vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin. And finally, patients taking warfarin should avoid eating an excess amount of leafy greens, and other foods high in vitamin K. Warfarin is also teratogenic and should not be given to pregnant patients. A therapeutic INR level for a patient on warfarin is between 2 and 3. To reduce the risk of severe bleeding, patients are monitored using the PT and INR levels. 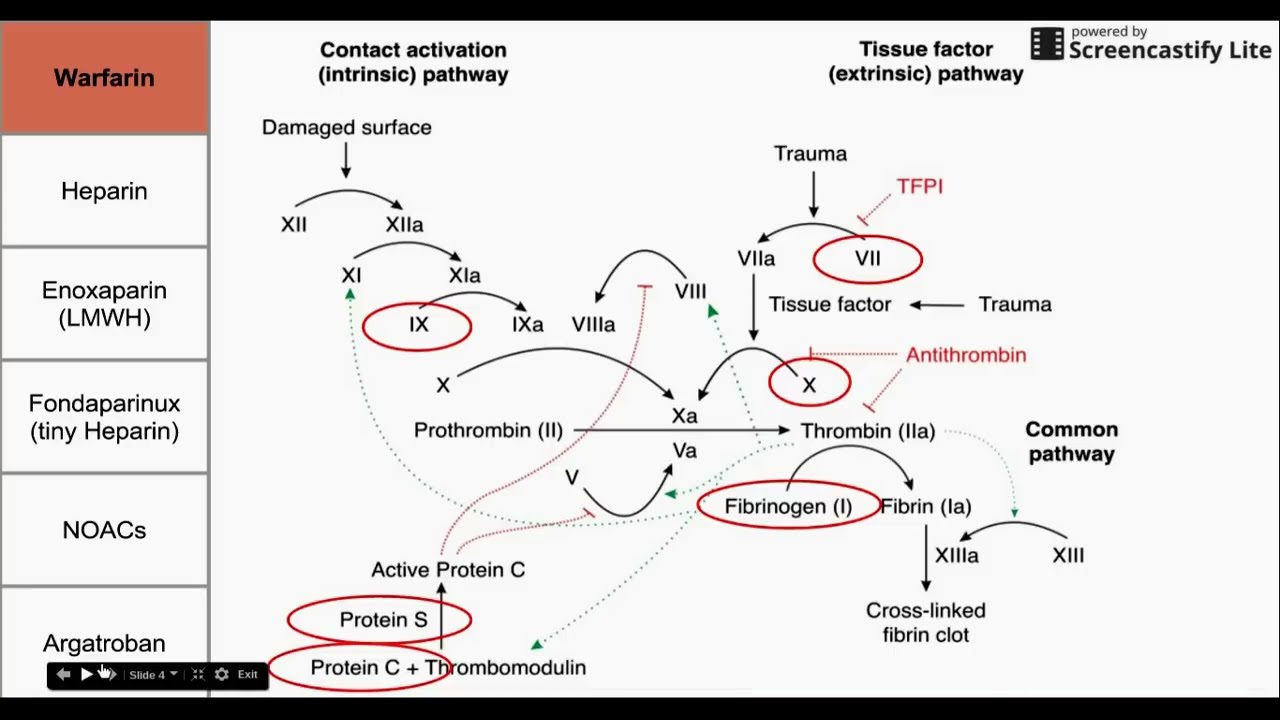
Along with its blood thinning action comes an increased risk for uncontrolled bleeding. Clinically, warfarin is used to prevent the formation of DVTs, pulmonary embolisms, heart attacks, and strokes in patients who are at high risk of developing blood clots. Summary Warfarin is a medication that is used to prevent blood clots, which is why it is classified as a blood thinner or anticoagulant.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
